Ubuntu 10.10
Objective
adduser
sudo
su
sudo -i
usermod
userdel
id
du
df
Summary
adduser command to create a new user account
su command to switch from one user to another
sudo -i command to change root password
usermod command for changing the user account setting
userdel command to delete the account
id command to know the information about user ids and group ids
df command to check the file system size and its availability
du command to check the space occupied by a file
adduser
The adduser command will create a new user login for us along with authentication
we can add any user account with the help of sudo command

sudo
sudo command allows the administrative user to execute a command as a super user.
The sudo command has many options.
Su
su stands for 'Switch User'
This commands is useful in switching from current user to another user.

sudo -i
sudo -i command which is user to change a root password

usermod
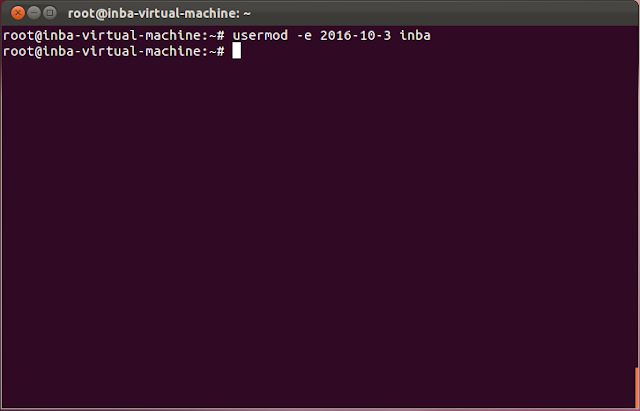
usermod Enables a super user or root user to modify the setting of others
user accounts:
change the password to no password or empty password
show the date on which the user
account will be disabled
userdel
we can delete the user account permanently with the help of the userdel command

id
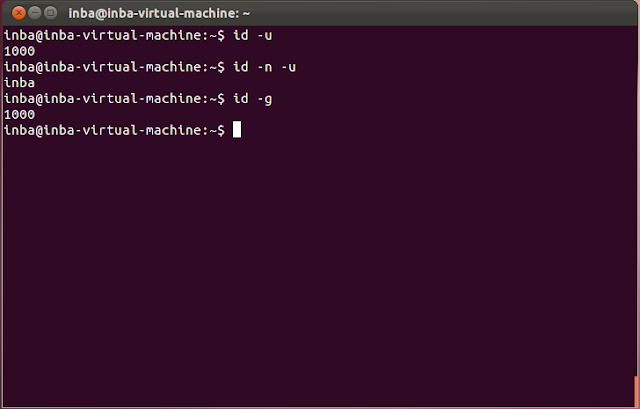
id command is used to check the identities of all the users and groups on the system
To know about the identity of the user, we use id -u
To know about the identity of the group users,it is id -g
df / du
The df command gives a report on the free space available on the disk.
The du command gives a report on how much space a file has occupied.

Objective
adduser
sudo
su
sudo -i
usermod
userdel
id
du
df
Summary
adduser command to create a new user account
su command to switch from one user to another
sudo -i command to change root password
usermod command for changing the user account setting
userdel command to delete the account
id command to know the information about user ids and group ids
df command to check the file system size and its availability
du command to check the space occupied by a file
adduser
The adduser command will create a new user login for us along with authentication
we can add any user account with the help of sudo command

sudo
sudo command allows the administrative user to execute a command as a super user.
The sudo command has many options.
Su
su stands for 'Switch User'
This commands is useful in switching from current user to another user.

sudo -i
sudo -i command which is user to change a root password

usermod
usermod Enables a super user or root user to modify the setting of others
user accounts:
change the password to no password or empty password
show the date on which the user
account will be disabled

userdel
we can delete the user account permanently with the help of the userdel command

id
id command is used to check the identities of all the users and groups on the system
To know about the identity of the user, we use id -u
To know about the identity of the group users,it is id -g

df / du
The df command gives a report on the free space available on the disk.
The du command gives a report on how much space a file has occupied.

No comments:
Post a Comment